Tathagata Sengupta(TCGLS Member), Rishi Das (TCGLS Member), Sumantra Chattarji
Neuroscience Letters (2016), 633, 101-105.
DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.09.031
Abstract: Acute stress has been shown to facilitate but not increase metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) mediated Long-Term Depression (LTD) in the hippocampus. However, the effect of chronic stress on mGluR dependent LTD has not been investigated. Moreover, whether stress leads to a transient modification LTD threshold or a more stable change in synaptic plasticity needs to be addressed. In the present study, we have explored the effects of both a ten-day long and a single day immobilization stress protocol on mGluR-LTD at the CA3:CA1synapse in the hippocampus of adult male Sprague-Dawley rats, a day after applying stress. Bath application of the selective group 1 mGluR agonist (S)-3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine (DHPG) promoted robust LTD in hippocampal slices from control (i.e. un-stressed) animals. Administration of immobility stress for two hours per day for ten days significantly elevated this LTD to a level almost twice that of control, when observed 24h following the last stress event. Acute stress i.e. a single day of two hours of immobilization, however, failed to significantly enhance LTD, 24h later. These results demonstrate for the first time, that repeated exposure to stress, but not a single stress event, is required to bring about a stable alteration in mGluR mediated synaptic plasticity.
Igawa Hideyuki; Takahashi Masashi; Shirasaki Mikio; Kakegawa Keiko; Kina Asato; Ikoma Minoru; Aida Jumpei; Okuda Shoki; Kawata Yayoi; Noguchi Toshihiro; Yamamoto Syunsuke; Fujioka Yasushi; Nakayama Masaharu; Kasai Shizuo; Maekawa Tsuyoshi; Yasuma Tsuneo; Kundu Mrinalkanti; Khamrai Uttam (TCGLS Member); Nagisa Yasutaka
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Volume 24, Issue 11, 1 June 2016, Pages 2486–2503
DOI : 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.04.011
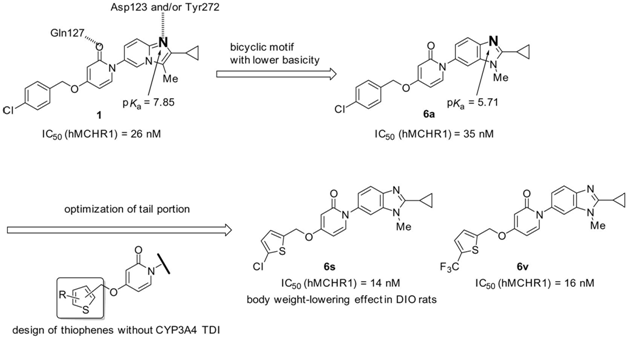
Abstract: Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) is an attractive target for antiobesity agents, and numerous drug discovery programs are dedicated to finding small-molecule MCH receptor 1 (MCHR1) antagonists. We recently reported novel pyridine-2(1H)-ones as aliphatic amine-free MCHR1 antagonists that structurally featured an imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-based bicyclic motif. To investigate imidazopyridine variants with lower basicity and less potential to inhibit cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), we designed pyridine-2(1H)-ones bearing various less basic bicyclic motifs. Among these, a lead compound 6a bearing a 1H-benzimidazole motif showed comparable binding affinity to MCHR1 to the corresponding imidazopyridine derivative 1. Optimization of 6a afforded a series of potent thiophene derivatives (6q-u); however, most of these were found to cause time-dependent inhibition (TDI) of CYP3A4. As bioactivation of thiophenes to form sulfoxide or epoxide species was considered to be a major cause of CYP3A4 TDI, we introduced electron withdrawing groups on the thiophene and found that a CF3 group on the ring or a Cl adjacent to the sulfur atom helped prevent CYP3A4 TDI. Consequently, 4-[(5-chlorothiophen-2-yl)methoxy]-1-(2-cyclopropyl-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-6-yl)pyridin-2(1H)-one (6s) was identified as a potent MCHR1 antagonist without the risk of CYP3A4 TDI, which exhibited a promising safety profile including low CYP3A4 inhibition and exerted significant antiobesity effects in diet-induced obese F344 rats.
Mahato, Chandan K. (TCGLS Member); Kundu, Mrinalkanti (TCGLS Member); Pramanik, Animesh (TCGLS Member)
Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2017, 28(4), 511-515
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetasy.2017.03.002
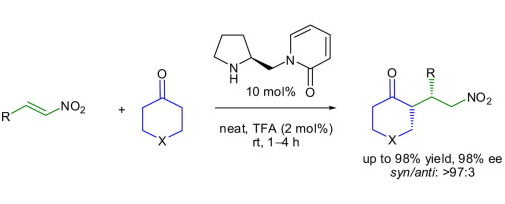
Abstract: New chiral organocatalysts are envisaged based on a pyrrolidine–pyridone conjugate and synthesized from commercially available proline employing standard protocols. These catalysts were found to be useful for asymmetric Michael additions of ketones to nitroolefins to afford the desired products in very good yields (up to 98%) with excellent diastereo- and enantioselectivities (>97:3 syn/anti and up to 98% ee) in very short reaction time compared with the existing reports
Schwertz Geoffrey; Siggel Marc; Zwyssig Adrian; Diederich Francois; Witschel Matthias C; Aponte Raphael A; Rottmann Matthias; Schafer Anja; Rottmann Matthias; Schafer Anja; Bonnert Roger; Leartsakulpanich Ubolsree; Chitnumsub Penchit; Jaruwat Aritsara; Ittarat Wanwipa; Charman Susan A; White Karen L; Kundu Abhijit (TCGLS Member); Sadhukhan Surajit (TCGLS Member); Lloyd Mel; Freiberg Gail M; Srikumaran Myron; Chaiyen Pimchai
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00008
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2017, 60(12), 4840-4860
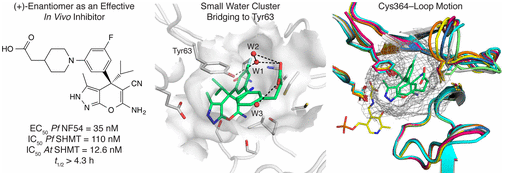
Abstract: Target-based approaches toward new antimalarial treatments are highly valuable to prevent resistance development. We report several series of pyrazolopyran-based inhibitors targeting the enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT), designed to improve microsomal metabolic stability and to identify suitable candidates for in vivo efficacy evaluation. The best ligands inhibited Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) and Arabidopsis thaliana (At) SHMT in target assays and PfNF54 strains in cell-based assays with values in the low nanomolar range (3.2-55 nM). A set of carboxylate derivatives demonstrated markedly improved in vitro metabolic stability (t1/2 > 2 h). A selected ligand showed significant in vivo efficacy with 73% of parasitemia reduction in a mouse model. Five new cocrystal structures with PvSHMT were solved at 2.3-2.6 ÅA resolution, revealing a unique water-mediated interaction with Tyr63 at the end of the para-aminobenzoate channel. They also displayed the high degree of conformational flexibility of the Cys364-loop lining this channel
Le Thuy G; Nguyen Nghi H; Ruan Banfeng; Baell Jonathan B; Kundu Abhijit (TCGLS Member); Ghoshal Atanu (TCGLS Member); Preston Sarah; Jiao Yaqing; Chang Bill C H; Garcia-Bustos Jose; Jabbar Abdul; Gasser Robin B; Preston Sarah; Ruan Banfeng; Xue Lian; Huang Fei; Baell Jonathan B; Keiser Jennifer; Keiser Jennifer; Hofmann Andreas; Wells Timothy N C; Palmer Michael J
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2018, 61(23), 10875-10894
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01544
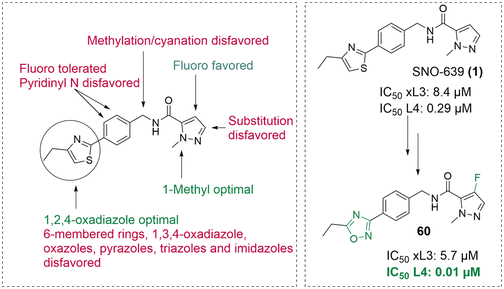
Abstract: A phenotypic screen of a diverse library of small molecules for inhibition of the development of larvae of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus led to the identification of a 1-methyl-1 H-pyrazole-5-carboxamide derivative with an IC50 of 0.29 μM. Medicinal chemistry optimization targeted modifications on the left-hand side (LHS), middle section, and right-hand side (RHS) of the scaffold in order to elucidate the structure-activity relationship (SAR). Strong SAR allowed for the iterative and directed assembly of a focus set of 64 analogues, from which compound 60 was identified as the most potent compound, inhibiting the development of the fourth larval (L4) stage with an IC50 of 0.01 μM. In contrast, only 18% inhibition of the mammary epithelial cell line MCF10A viability was observed, even at concentrations as high as 50 μM
Pati Tanmay K (TCGLS Member); Debnath Sudipto; Maiti Dilip K; Kundu Mrinalkanti (TCGLS Member); Khamrai Uttam (TCGLS Member)
Organic Letters 2018 20(13), 4062-4066
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01618
Abstract: A new bidentate directing group, 3-amino-1-methyl-1 H-pyridin-2-one, is introduced to achieve a powerful Pd(II) metallacycle for selective γ-C(sp(3))-H activation and arylation of aromatic and aliphatic carboxylic acid derivatives. The versatility of the directing group is validated for remote arylation of β-C(sp(3))-H, β-C(sp(2))-H, and γ-C(sp(2))-H to achieve therapeutically important 2-pyridone analogues and arylated acid synthons. The traceless removal of the directing group to retrieve the directing element and carboxylic acids makes this method more interesting.
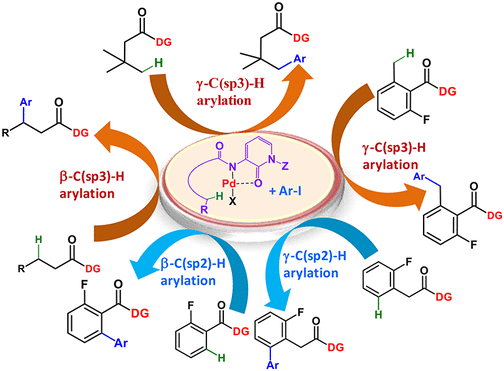
Chandan K. Mahato (TCGLS Member), Sayan Mukherjee, Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member), and Animesh Pramanik
The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2019 84 (2), 1053-1063
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b02393
Abstract
Pyrrolidine-oxadiazolone based organocatalysts are envisaged, synthesized, and utilized for asymmetric Michael reactions. Results of the investigations suggest that some of the catalysts are indeed efficient for stereoselective 1,4-conjugated Michael additions (dr: >97:3, ee up to 99%) in high chemical yields (up to 97%) often in short reaction time. As an extension, one enantiopure Michael adduct has been utilized to synthesize optically active octahydroindole.

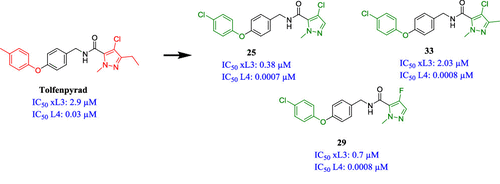
Thuy G. Le, Abhijit Kundu (TCGLS Member), Atanu Ghoshal (TCGLS Member), Nghi H. Nguyen, Sarah Preston, Yaqing Jiao, Banfeng Ruan, Lian Xue, Fei Huang, Jennifer Keiser, Andreas Hofmann, Bill C. H. Chang, Jose Garcia-Bustos, Timothy N. C. Wells, Michael J. Palmer, Abdul Jabbar, Robin B. Gasser, and Jonathan B. Baell
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2019 62 (2), 1036-1053
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01789
Abstract
Recently, we have discovered that the registered pesticide, tolfenpyrad, unexpectedly and potently inhibits the development of the L4 larval stage of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus with an IC50 value of 0.03 μM while displaying good selectivity, with an IC50 of 37.9 μM for cytotoxicity. As a promising molecular template for medicinal chemistry optimization, we undertook anthelmintic structure–activity relationships for this chemical. Modifications of the left-hand side (LHS), right-hand side (RHS), and middle section of the scaffold were explored to produce a set of 57 analogues. Analogues 25, 29, and 33 were shown to be the most potent compounds of the series, with IC50 values at a subnanomolar level of potency against the chemotherapeutically relevant fourth larval (L4) stage of H. contortus. Selected compounds from the series also showed promising activity against a panel of other different parasitic nematodes, such as hookworms and whipworms.
Pseudo five component reaction towards densely functionalized spiro[indole-3,2′-pyrrole] by picric acid, an efficient syn-diastereoselective catalyst: insight into the diastereoselection on C(sp3)–C(sp3) axial conformation.
Ayon Sengupta (TCGLS Member) Suvendu Maity, Animesh Mondal, Prasanta Ghosh, Sonali Rudra (TCGLS Member) and Chhanda Mukhopadhyay
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019,17, 1254-1265
DOI: 10.1039/C8OB02849D
Abstract
A new series of highly-functionalized spiro compounds of pyrrole were synthesized by a one pot, step-economic condensation of isatin, arylamine and β-keto ester catalyzed by wet picric acid. Initially, the reaction was proposed with an expectation of the formation of a multi-spiro heterocyclic framework of highly-substituted piperidine. However, the isomeric compound was characterized to be a five-membered pyrrole derivative with a diverse scope of variations having different types of substituents in the three components respectively. The possibility of formation of various diastereomers around the hindered single bond and the spiro carbon was limited, as only syn products syn-60 and syn-60′ were isolated in all the reactions performed under the standard conditions. Probably the reactions were mediated by the si-facial formation of the bonds in a picric acid stabilized charge transfer complex transition state. Also, the manner a molecule achieves the most stabilized energy minimized arrangement with all its substituents in space was studied by DFT calculations where syn-60 was more stable than syn-60′. The studies on the formation of syn-60 and syn-60′ were carried out by variation of electronic and steric factors in each of the components of the reactions.

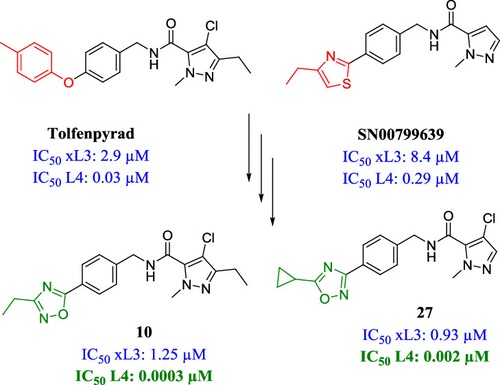
Thuy G. Le, Abhijit Kundu (TCGLS Member), Atanu Ghoshal (TCGLS Member), Nghi H. Nguyen, Sarah Preston, Yaqing Jiao, Banfeng Ruan, Lian Xue, Fei Huang, Jennifer Keiser, Andreas Hofmann, Bill C. H. Chang, Jose Garcia-Bustos, Timothy N. C. Wells, Michael J. Palmer, Abdul Jabbar, Robin B. Gasser, and Jonathan B. Baell
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2019 62 (7), 3367-3380
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01790
Abstract: A phenotypic screen of two different libraries of small molecules against the motility and development of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus led to the identification of two 1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamide derivatives. Medicinal chemistry optimization-targeted modifications of the left-hand side, middle section, and right-hand side of the hybrid structure of these two hits to elucidate the structure-activity relationship (SAR). Initial SAR around these hits allowed for the iterative and directed assembly of a focused set of 30 analogues of their hybrid structure. Compounds 10, 17, 20, and 22 were identified as the most potent compounds, inhibiting the development of the fourth larval (L4) stage of H. contortus at sub-nanomolar potencies while displaying strong selectivity toward the parasite when tested in vitro against the human MCF10A cell line. In addition, compounds 9 and 27 showed promising activity against a panel of other parasitic nematodes, including hookworms and whipworms.












.jpg ?>)
.jpg ?>)
