Published in: Journal, Article, Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t, Volume : 64, Issue : 1, Pages : 840-844
DOI : 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01793
Author : Preston, Sarah; Garcia-Bustos, Jose; Hall, Liam G.; Martin, Sheree D.; Le, Thuy G.; Kundu, Abhijit; Ghoshal, Atanu; Nguyen, Nghi H.; Jiao, Yaqing; Ruan, Banfeng; Xue, Lian; Huang, Fei; Chang, Bill C. H.; McGee, Sean L.; Wells, Timothy N. C.; Palmer, Michael J.; Jabbar, Abdul; Gasser, Robin B.; Baell, Jonathan B.
Abstract : A series of 1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamides were synthesized as potent inhibitors of the parasitic nematode of sheep, Haemonchus contortus. These compounds did not show overt cytotoxicity to a range of mammalian cell lines under standard in vitro culture conditions, had high selectivity indexes, and were progressed to an acute toxicity study in a rodent model. Strikingly, acute toxicity was observed in mice. Experiments measuring cellular respiration showed a dose-dependent inhibition of mitochondrial respiration. Under these conditions, potent cytotoxicity was observed for these compounds in rat hepatocytes suggesting that the potent acute mammalian toxicity of this chemotype is most likely associated with respiratory inhibition. In contrast, parasite toxicity was not correlated to acute toxicity or cytotoxicity in respiring cells. This paper highlights the importance of identifying an appropriate in vitro predictor of in vivo toxicity early on in the drug discovery pipeline, in particular assessment for in vitro mitochondrial toxicity.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0OB02134B
Palladium catalyzed arylation of the inert β-C(sp2)–H bond of carboxylic acid derivatives is reported herein for the first time utilizing 8-aminoimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine (AIP) as an efficacious and new inbuilt 6,5-fused bicyclic removable directing group. This protocol is scalable, exhibits high levels of β-site selectivity and tolerates a broad spectrum of functional groups.
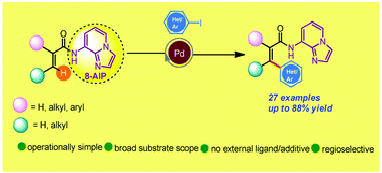
Authors: Biswajit Mondal (TCGLS Member), Prasanjit Ghosh, Mrinalkanti Kundu* (TCGLS Member), Tapas Kumar Das (TCGLS Member), Sajal Das*
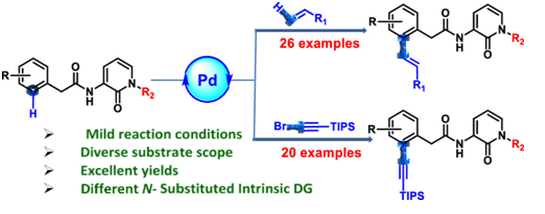
Authors: Tanmay K. Pati (TCGLS Member), Sk Ajarul, Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member), Deepak Tayde, Uttam Khamrai (TCGLS Member),* and Dilip K. Maiti*
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.0c00941
We have identified different N-substituted 2-pyridones as inbuilt directing groups for selective C–H-activated functionalization instead of deprotecting and/or throwing away the directing groups. A robust general method for external ligand-free PdII-catalyzed C¬(sp2)–H olefination and alkynylation is established to access valuable phenylacetamido-2-pyridones. Diverse substrate scope has been demonstrated with 48 different examples with high yield and gram-scale synthesis. Adequate tolerance of valuable functional groups was also observed, such as olefins possessing esters, sulfone, amide, cyanide, and ketones, aromatic residues containing fluorine, chlorine, bromine, NO2, methyl, dimethyl, and methoxy, as well as 2-pyridone-N-bearing methyl, cyclopropyl methyl, cyclopentyl methyl, benzyl, phenyl, acetate, and acetamide groups, which smoothly produced the respective desired products. We used triisopropyl silane-substituted alkynes for the alkynylation reaction, which can easily be converted to several functional groups including terminal alkyne, heterocycle through click reaction, and others. Implementing our protocol, we have also demonstrated late-stage olefination and alkynylation of 2-pyridone, containing the CB2 agonist-type molecule with excellent yield. Considering N-substituted 2-pyridone acts as a biologically-active structural unit, this general method has the significance in terms of late-stage functionalization to access new molecular entities which can be employed in medicinal chemistry research through diverse C–H activation.
Authors : Rishi Das [TCGLS Member], Tathagata Sengupta [TCGLS Member], Shubhrajit Roy, Sumantra Chattarji, Jharna Ray
DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001446
The memory-boosting property of Indian traditional herb, Convolvulus pluricaulis, has been documented in literature; however, its effect on synaptic plasticity has not yet been reported. Two important forms of synaptic plasticity known to be involved in the processes of memory formation are long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). In the present study, the effect of C. pluricaulis plant extract on LTP and LTD were evaluated. The adult male Wistar rats were fed orally with 250, 500 and 1000 mg/kg of this extract for 4 weeks and the effect was determined on LTP and LTD in the Schaffer collaterals of the hippocampal cornu ammonis region CA1. We found that the 500 mg/kg dose of the extract could significantly enhance LTP compared to the vehicle treated ones. Moreover, the same dose could also reduce LTD while used in a separate set of animals. Also, a fresh group of animals treated with the effective dose (500 mg/kg) of plant extract were examined for memory retention in two behavioral platforms namely, contextual fear conditioning (CFC) and novel object recognition test (NORT). Increased fear response to the conditioned stimulus and enhanced recognition of objects were observed in CFC and NORT, respectively, both indicating strengthening of memory. Following up, ex-vivo electrophysiology experiments were performed with the active single molecule scopoletin, present in C. pluricaulis extract and similar patterns in synaptic plasticity changes were obtained. These findings suggest that prolonged treatment of C. pluricaulis extract, at a specific dose in healthy animals, can augment memory functions by modulating hippocampal plasticity..
Ashis Roy (TCGLS Member), Dr. Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member), Dr. Pranab Dhar (TCGLS Member), Arnish Chakraborty (TCGLS Member), Dr. Soumen Mukherjee (TCGLS Member), Jayatri Naskar (TCGLS Member), Dr. Chhanda Rarhi (TCGLS Member), Dr. Rajib Barik (TCGLS Member), Dr. Susanta Kumar Mondal (TCGLS Member), Mushtaq Ahmad Wani, Rahul Gajbhiye, Prof. Kuldeep K. Roy, Dr. Arup Maiti (TCGLS Member), Priyadarshi Manna (TCGLS Member), Prof. Susanta Adhikari
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202000208
Abstract
A series of novel bicyclic, substituted pyrimidinone compounds were designed, synthesized, and characterized. In vitro anti‐proliferative activity of the synthesized compounds was evaluated against six different human cancer cell lines using MTT assay. Among all twenty-four compounds tested, compound 22 (N‐([1,1′‐biphenyl]‐4‐yl)‐2‐((3‐methyl‐4‐oxo‐6,7,8,9‐tetrahydro‐4Hpyrido[1,2‐a]pyrimidin‐2‐yl)oxy)acetamide) exhibited significant cell growth inhibition of human liver cancer cells HepG2 with GIC50 (50% growth inhibitory concentration) value of 120+10 nM and was found to be selective over healthy human embryonic kidney (HEK) cell line (33.1% inhibition at 20 μM). Further studies demonstrated that compound 22 induced cell apoptosis in HepG2 cells and resulted in a similar effect to Staurosporine, a well known proapoptotic compound widely used to induce apoptosis in various cancer cell lines. Compound 22 also rendered acceptable aqueous solubility (3.5+0.37 μM, at pH 7.4) and attractive metabolic stability against human liver microsomes with a half‐life of 34.63+0.33 minutes. Based on the similarity observed between the known tankyrase‐1 inhibitors available in the literature and compound 22, in silico docking study was performed and the results suggested that the compound interacted with the key amino acid residues present in the tankyrase‐1 enzyme active site.
Published in: Journal Volume : 502, Pages : 119286
DOI : 10.1016/j.ica.2019.119286
Author : Asthana, Mrityunjaya; Syiemlieh, Ibanphylla; Kumar, Arvind; Lal, Ram A.
Abstract : A ligand and additive-free [CuNi(bz)3(bpy)2]ClO4 catalyst system that efficiently and selectively catalyzed the oxidation of a range of primary and secondary benzylic alcs., 1-heteroaryl alcs., cinnamyl alc. and aliphatic alcs. mediated by hydrogen peroxide to the corresponding aldehydes and ketones, resp.
Published in: Journal, General Review, Article, Review Volume : 5, Issue : 6, Pages : 2503-2519
DOI : 10.1021/acsomega.9b03686
Author : Mahato, Sanjit K.; Acharya, Chiranjit; Wellington, Kevin W.; Bhattacharjee, Pinaki; Jaisankar, Parasuraman
Abstract : A review. This review deals with the recent applications of the indium trichloride (InCl3) catalyst in the synthesis of a broad spectrum of heterocyclic compounds Over the years, a number of reviews on the applications of InCl3-catalyzed organic synthesis have appeared in the literature. It is evident that InCl3 has emerged as a valuable catalyst for a wide range of organic transformations due to its stability when exposed to moisture and also in an aqueous medium. The most attractive feature of this review is the application of the InCl3 catalyst for synthesizing bioactive heterocyclic compounds The study of InCl3-catalyzed organic reactions has high potential and better intriguing aspects, which are anticipated to originate from this field of research.
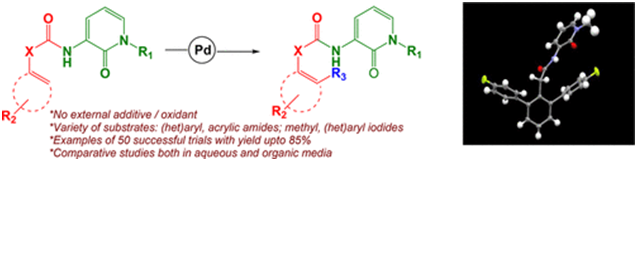
Trisha Mitra (TCGLS Member), Brindaban Roy and Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member)
The Journal of organic chemistryJournal; Article; (JOURNAL ARTICLE), 2019
DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b02122
Small molecules containing a 2-pyridone unit received much attention due to their significance in medicinal chemistry. In this regard, development of novel methodologies via metal-catalyzed carbon-carbon bond formation by chelation-assisted C-H activation will be an attractive method to achieve therapeutically important 2-pyridone analogues and arylated acid synthons. We report our studies on a Pd(II)-catalyzed coupling reaction between methyl, aryl, heteroaryl iodides, and sp(2) carbons both at β- and γ-positions using 3-amino-1-methyl-1H-pyridin-2-one as an efficient, built-in bidentate N,O-directing group (DG) toward the synthesis of pyridone derivatives. The effect of temperature, solvent, reagent equivalence, and substrate has been investigated for this DG-mediated late-stage functionalization reactions along with the crystal structure of a selected analogue. Moreover, this DG has been successfully applied for ortho-selective C(sp(2))-H activation in aqueous medium in high yields to demonstrate the practicability of this present methodology.
Bhawana Gupta (TCGLS Member), Sabyasachi Chakraborty (TCGLS Member), Soumya Saha (TCGLS Member), Sunita Chandel (TCGLS Member), Gulab Singh (TCGLS Member), Atul Kumar Baranwal (TCGLS Member), Manish Banerjee (TCGLS Member), Mousumi Chatterjee (TCGLS Member), Ashok Chaudhury.
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology Volume 94 Issue 7 Pages 788-796, 1996
DOI: 10.1139/cjpp-2015-0465
Shikonin possess a diverse spectrum of Pharmacol. properties in multiple therapeutic areas. However, the nociceptive effect of shikonin is not largely known. To investigate the antinociceptive potential of shikonin, panel of GPCRs, ion channels, and enzymes involved in pain pathogenesis were studied. To evaluate the translation of shikonin efficacy in vivo, it was tested in 3 established rat pain models. Our study reveals that shikonin has significant inhibitory effect on pan sodium channel/N1E115 and NaV1.7 channel with half maximal inhibitory concn. (IC50) value of 7.6 μmol/L and 6.4 μmol/L, resp., in a cell-based assay. Shikonin exerted significant dose dependent antinociceptive activity at doses of 0.08%, 0.05%, and 0.02% w/v in pinch pain model. In mech. hyperalgesia model, dose of 10 and 3 mg/kg (i.p.) produced dose-dependent analgesia and showed 67% and 35% reversal of hyperalgesia resp. at 0.5 h. Following oral administration, it showed 39% reversal at 30 mg/kg dose. When tested in first phase of formalin induced pain, shikonin at 10 mg/kg dose inhibited paw flinching by ∼71%. In all studied preclin. models, analgesic effect was similar or better than std. analgesic drugs. The present study unveils the mechanistic role of shikonin on pain modulation, predominantly via sodium channel modulation, suggesting that shikonin could be developed as a potential pain blocker
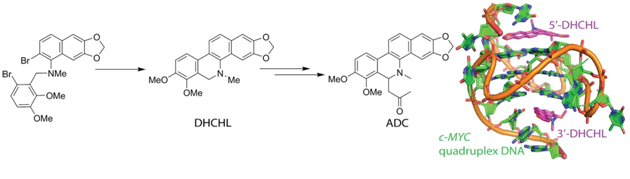
Rajesh Malhotra, Chhanda Rarhi (TCGLS Member), K V Diveshkumar, Ruhee D’cunha, Rajib Barik( TCGLS Member), Pranab Dhar (TCGLS Member), Subrata Chattopadhyay (TCGLS Member), Subho Roy (TCGLS Member), Sourav Basu, Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member), P I Pradeepkumar, Saumen Hajra
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Volume 24, Issue 13, 1 July 2016, Pages 2887–2896
DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.04.059
A convenient route was envisaged toward the synthesis of dihydrochelerythrine (DHCHL), 4 by intramolecular Suzuki coupling of 2-bromo-N-(2-bromobenzyl)-naphthalen-1-amine derivative 5 via in situ generated arylborane. This compound was converted to (±)-6-acetonyldihydrochelerythrine (ADC), 3 which was then resolved by chiral prep-HPLC. The efficiency of DHCHL for the stabilization of promoter quadruplex DNA structures and a comparison study with the parent natural alkaloid chelerythrine (CHL), 1 was performed. A thorough investigation was carried out to assess the quadruplex binding affinity by using various biophysical and biochemical studies and the binding mode was explained by using molecular modeling and dynamics studies. Results clearly indicate that DHCHL is a strong G-quadruplex stabilizer with an affinity similar to that.
at of the parent alkaloid CHL. Compounds ADC and DHCHL were also screened against different human cancer cell lines. Among the cancer cells, (±)-ADC and its enantiomers showed varied (15-48%) inhibition against human colorectal cell line HCT116 and breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 albeit low enantio-specificity in the inhibitory effect; whereas DHCHL showed 30% inhibition against A431 cell line only, suggesting the compounds are indeed cancer tissue-specific.







.jpg ?>)
.jpg ?>)
