Sameer Tyagi, Bruce P. McKillican, Tolani K. Salvador, Moses G. Gichinga, William J. Eberle, Russell Viner, Katarina J. Makaravage, Trey S. Johnson, C. Adam Russell, and Subho Roy (TCGLS Member)
Publication: J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 9, 6202–6211
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.2c00440
Abstract: A bioinspired synthesis of Pinoxaden metabolites 2–5 is described herein. A site-selective C–H oxidation strategy validated by density functional theory (DFT) calculations was devised for preparing metabolites 2–4. Oxidation of the benzylic C–H bond in tertiary alcohol 7 using K2S2O8 and catalytic AgNO3 formed the desired metabolite 2 that enabled access to metabolites 3 and 4 in a single step. Unlike most metal/persulfate-catalyzed transformations reported for the C–C and C–O bond formation reactions wherein the metal acts as a catalyst, we propose that Ag(I)/K2S2O8 plays the role of an initiator in the oxidation of intermediate 7 to 2. Metabolite 2 was subjected to a ruthenium tetroxide-mediated C–H oxidation to form metabolites 3 and 4 as a mixture that were purified to isolate pure standards of these metabolites. Metabolite 5 was synthesized from readily available advanced intermediate 9via a House–Meinwald-type rearrangement in one step using a base.

Ayon Sengupta (TCGLS Member), Suvendu Maity, Pinaki Saha, Prasanta Ghosh, Sonali Rudra (TCGLS Member), Chhanda Mukhopadhyay
Publication: Mol Divers. 2022 Aug 1. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10496-4. Online ahead of print
DOI: 10.1007/s11030-022-10496-4
Abstract: Petasis aryl and allyl borations were accomplished using substituted ninhydrins, boronic acids or 2-allyl-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane and 1,2-aminophenols in Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) without any catalysts to synthesize different aryl and allyl derivatives of ninhydrins. The nature of substitution in the boronic acids and 1,2-amino phenols was the key factor in determining the diastereo-regioselectivity and the type of product distributions. The products were isolated and characterized by HMBC, HSQC, 1H, 13C NMR experiments and X-ray single crystallographic analysis. A probable reaction pathway involves in situ formation of acyclic and cyclic ninhydrin-amino alcohol adducts, with the positioned hydroxyl group determining the stereo-regioselective outcome via tetracoordinated boron intermediates. A metal free diastereo- and regioselective Petasis aryl and allyl boration of ninhydrins
Kundu Mrinalkanti (TCGLS Member); Dutta Aditi (TCGLS Member); Mal Sajal K (TCGLS Member); Karmakar Shouvik (TCGLS Member); Mandal Aritra (TCGLS Member); Mondal Susanta K (TCGLS Member); Kumar Sanjay (TCGLS Member); Saha Soumya (TCGLS Member); Pradhan Subhankar (TCGLS Member); Sarkar Ratul (TCGLS Member); Chakrabarti Monali (TCGLS Member); Malik Pradip K (TCGLS Member); Banerjee Manish (TCGLS Member); Roy Kuldeep K
Publication: Chemical biology & drug design, ASAP
DOI: 10.1111/cbdd.14170
Abstract: Malaria continues to be a significant public health problem threatened by the emergence and spread of resistance to artemisinin-based combination therapies and marked half a million deaths in 2016. A new imidazopyridine chemotype has been envisaged through scaffold-hopping approach combined with docking studies for putative binding interactions with Plasmodium falciparum phosphatidylinositol-4-kinase (PfPI4K) target. The docking results steered to the synthesis of compound 1 [5-(3-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine] followed by the in vitro screening for antiplasmodial activity and ADME-PK studies. Combined with potent antimalarial activity of compound 1 (Pf3D7 IC50 = 29 nM) with meager in vitro intrinsic clearance, moderate plasma-protein binding and acceptable permeability, compound 1 displayed sustained exposure and high oral bioavailability in mice and can thus have the potential as next generation PI4K inhibitor for in vivo studies.
Tapas Kumar Das (TCGLS Member), Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member), Biswajit Mondal (TCGLS Member), Prasanjit Ghosh and Sajal Das
Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry 2022,20, 208-218 (Published on 30th Nov 2021)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1OB01798E
Abstract: A unique N,O-bidentate ligand 6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-pyridone-2-carboxylic acid dimethylamide (L1) catalyzed direct C(sp2)–H (intra/intermolecular) arylation of unactivated arenes has been developed to expedite access to (Het)biaryl scaffolds under UV-irradiation at room temperature. The protocol tolerated diverse functional groups and substitution patterns, affording the target products in moderate to excellent yields. Mechanistic investigations were also carried out to better understand the reaction pathway. Furthermore, the synthetic applicability of this unified approach has been showcased via the construction of biologically relevant 4-quinolone, tricyclic lactam and sultam derivatives.
Ashis Roy (TCGLS Member), Tonmoy Sarkar (TCGLS Member), Sebak Datta (TCGLS Member), Arup Maiti (TCGLS Member), Monali Chakrabarti (TCGLS Member), Trisha Mondal (TCGLS Member), Chaitali Mondal (TCGLS Member), Apurba Banerjee (TCGLS Member), Subhasis Roy (TCGLS Member), Soumen Mukherjee (TCGLS Member), Pragati Muley (TCGLS Member), Sabyasachi Chakraborty (TCGLS Member), Manish Banerjee (TCGLS Member), Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member), Kuldeep K. Roy
Chemical Biology and Drug Design, Volume99, Issue3 March 2022 Pages 496-503 (Published on 24th Dec 2021)
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.14017
Abstract: Inhibition of extracellular secreted enzyme autotaxin (ATX) represents an attractive strategy for the development of new therapeutics to treat various diseases and a few inhibitors entered in clinical trials. We herein describe structure-based design, synthesis, and biological investigations revealing a potent and orally bioavailable ATX inhibitor 1. During the molecular docking and scoring studies within the ATX enzyme (PDB-ID: 4ZGA), the S-enantiomer (Gscore = −13.168 kcal/mol) of the bound ligand PAT-494 scored better than its R-enantiomer (Gscore = −9.562 kcal/mol) which corroborated with the reported observation and analysis of the results suggested the scope of manipulation of the hydantoin substructure in PAT-494. Accordingly, the docking-based screening of a focused library of 10 compounds resulted in compound 1 as a better candidate for pharmacological studies. Compound 1 was synthesized from L-tryptophan and evaluated against ATX enzymatic activities with an IC50 of 7.6 and 24.6 nM in biochemical and functional assays, respectively. Further, ADME-PK studies divulged compound 1 as non-cytotoxic (19.02% cell growth inhibition at 20 μM in human embryonic kidney cells), metabolically stable against human liver microsomes (CLint = 15.6 μl/min/mg; T1/2 = 113.2 min) with solubility of 4.82 μM and orally bioavailable, demonstrating its potential to be used for in vivo experiments.
Sarabindu Roy (TCGLS Member), Ajay Yadaw (TCGLS Member), Subho Roy (TCGLS Member), Gopal Sirasani (TCG GC Member), Aravind Gangu (TCG GC Member), Jack D. Brown (TCG GC Member), Joseph D. Armstrong III (TCG GC Member), Rodger W. Stringham, B. Frank Gupton, Chris H. Senanayake* (TCG GC Member), and David R. Snead*Organic Process Research and Development (Published on 07th Jan 2022)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.1c00071
Abstract: Pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazine (1) is an important regulatory starting material in the production of the antiviral drug remdesivir. Compound 1 was produced through a newly developed synthetic methodology utilizing simple building blocks such as pyrrole, chloramine, and formamidine acetate by examining the mechanistic pathway for the process optimization exercise. Triazine 1 was obtained in 55% overall yield in a two-vessel-operated process. This work describes the safety of the process, impurity profiles and control, and efforts toward the scale-up of triazine for the preparation of kilogram quantity.
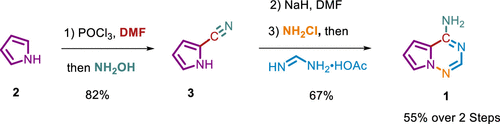
Priyadarshi Manna (TCGLS Member); Mrinalkanti Kundu (TCGLS Member); Ashis Roy (TCGLS Member);Susanta Adhikari
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1039/D1OB00663K
Abstract: The synthesis of deuterium-labeled organic compounds is of increased interest, especially after the approval of deutetrabenazine by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014. The selective incorporation of deuterium in the place of hydrogen not only represents uniqueness in terms of a novel chemical class, but it also can improve the pharmacokinetic profiles of drug molecules while retaining potency and other parameters; thus, hydrogen–deuterium (H/D) exchange methods have been proven to be powerful additions in different areas of chemical science. In that regard, metal-catalyzed deuterium labeling via C–H activation mediated by a unique inbuilt directing group (DG) can play a significant role in the synthesis of novel deuterated chemical entities. In this context, herein, we divulge our results relating to Pd(II)-catalyzed deuterium incorporation (>97%) at the γ C(sp2)-position of pyridone-containing phenylacetic acid derivatives, where 3-amino-1-methyl-1H-pyridin-2-one (AMP) not only acts as an efficient N,O-directing group, but it also constitutes a part of the target molecules of medicinal importance. Our methodology, which has been optimized based on the effects of temperature, catalyst, time, and substrate scope, shows advantages over existing protocols, with non-selectivity or meager deuteration or the use of an expensive metal (catalytic or super stoichiometric) and a deuterated solvent, reported previously for the deuteration of phenylacetic acid and its derivatives. Moreover, towards our aim of synthesizing deuterium-labeled biologically relevant compounds, the gram scale synthesis of a deuterated analogue of biphenyl acetic acid (3), known to have activity against epileptic seizures, has also been successfully accomplished in high yields and with excellent isotope enrichment via implementing this protocol.
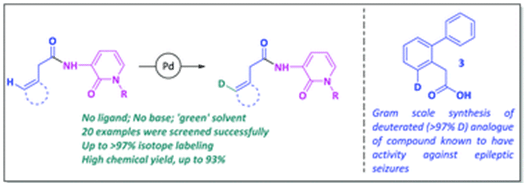
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c00124
Abstract: Org. transformations exclusively in water as an environmentally friendly and safe medium have drawn significant interest in the recent years. Moreover, transition metal-free synthesis of enantiopure mols. in water will have a great deal of attention as the system will mimic the natural enzymic reactions. In this work, a new set of proline-derived hydrophoborganocatalysts have been synthesized and utilized for asym. Michael reactions in water as the sole reaction medium. Among the various catalysts screened, the catalyst 1 is indeed efficient for stereoselective 1,4-conjugated
Michael addns. (dr: >97:3, ee up to >99.9%) resulting in high chem. yields (up to 95%) in a very short reaction time (1 h) at room temp. This methodol. provides a robust, green, and convenient protocol and can thus be an important addn. to the arsenal of the asym. Michael addn. reaction. Upon successful implementation, the present strategy also led to the formation of an optically active octahydroindole, the key component found in many natural products.
Graphical Abstract:-
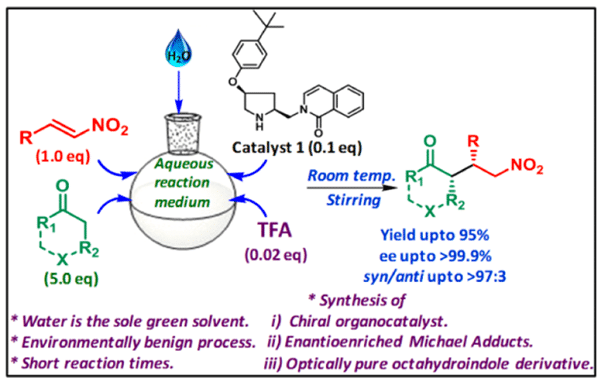
Authors: Chandan K Mahato (TCGLS Member); Satan Mukherjee, Mrinalkanti Kundu* (TCGLS Member); Virbhadra P. Vallapure, Animesh Pramanik
Biswajit Mondal (TCGLS Member); Prasanjit Ghosh; Mrinalkanti Kundu; (TCGLS Member); Sajal Das
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1039/D0OB02510K
Abstract: We demonstrate herein the first example of a palladium(II) catalyzed regioselective ortho-C(sp2)–H arylation in aqueous medium (a sustainable solvent) utilizing 8-AIP (8-aminoimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine) as a promising and removable bidentate directing group/auxilliary. This newly developed protocol features a broad substrate scope with excellent functional group tolerance and enables an expeditious route to a library of unsymmetrical amides in good to excellent yields with exclusive site-selectivity
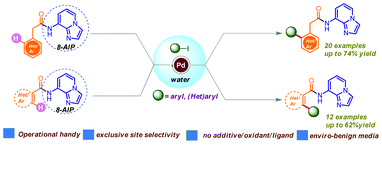
Published in: Journal, Article, Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t Volume : 16, Issue : 3, Pages : 484-498
DOI : 10.1002/cmdc.202000564
Author : Yasmin, Sabina; Cerchia, Carmen; Badavath, Vishnu Nayak; Laghezza, Antonio; Dal Piaz, Fabrizio; Mondal, Susanta K.; Atli, Oezlem; Baysal, Merve; Vadivelan, Sankaran; Shankar, S.; Siddique, Mohd. Usman Mohd.; Pattnaik, Ashok Kumar; Singh, Ravi Pratap; Loiodice, Fulvio; Jayaprakash, Venkatesan; Lavecchia, Antonio
Abstract : Insulin resistance is a major pathophysiol. feature in the development of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Ferulic acid is known for attenuating the insulin resistance and reducing the blood glucose in T2DM rats. In this work, we designed and synthesized a library of new ferulic acid amides (FAA), which could be considered as ring opening derivatives of the antidiabetic PPARγ agonists Thiazolidinediones (TZDs). However, since these compounds displayed weak PPAR transactivation capacity, we employed a proteomics approach to unravel their mol. target(s) and identified the peroxiredoxin 1 (PRDX1) as a direct binding target of FAAs. Interestingly, PRDX1, a protein with antioxidant and chaperone activity, has been implied in the development of T2DM by inducing hepatic insulin resistance. SPR, mass spectrometry-based studies, docking experiments and in vitro inhibition assay confirmed that compounds (I) and (II) bound PRDX1 and induced a dose-dependent inhibition. Furthermore, I and II significantly improved hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in streptozotocin-nicotinamide (STZ-NA)-induced diabetic rats as confirmed by histopathol. examinations These results provide guidance for developing the current FAAs as new potential antidiabetic agents.








.jpg ?>)
.jpg ?>)
