Md. Akram Ali (TCGLS Member), Rajib Chakraborty (TCGLS Member), Susanta Kumar Mondal (TCGLS Member). Supriya Bhunia, Sabyasachi Chakraborty (TCGLS Member), Subhas Samanta, Sonali Rudra (TCGLS Member)
Publication: Journal of Molecular Structure Volume 1260, 15 July 2022, 132730
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132730
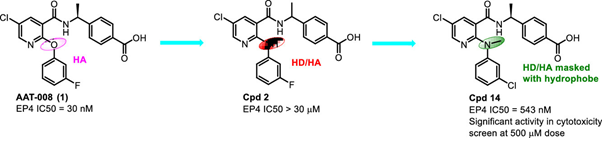
Abstract: Selective binding of the pleiotropic lipid mediator prostanoid Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) towards the G-protein coupled EP4 receptor has been studied extensively for inflammatory and hyperalgesia models and has been implicated to have significant potential for the treatment of various forms of cancers. Interest of nicotinamides as EP4 antagonists for oncology research, led us to synthesize a small set of molecules using the nicotinamide derivative AAT-008 (1) as our starting point for design. Subtle changes by replacing the hydrogen bond accepting bi-aryl-ether moiety in (1) to hydrogen bond donating bi-aryl-amino moiety and thereafter modifications on the substituents in the bi-aryl ring systems, carboxyl and the amino groups enabled us to identify a modestly potent new EP4 antagonist compound 14 with IC50 = 0.543 ± 0.148 μM (n = 6). Compound 14 was found to be stable in ADME assays and had reasonably good solubility. The interplay of electronic parameters such as lipohilicity and polarity of the compounds did not seem to play a significant role in deriving the EP4 antagonism potency for these compounds. Thus, molecular docking studies were carried out to understand the structure activity relationships (SAR). The trend in activity range of the synthesized compounds and the lower EP4 activity of compound 14 in contrast to compound 1 was explained with aid of molecular docking studies that supported our experimental potency results also. Preliminary screening of compounds 1 and 14 for oncology showed weak activity at a modest dose of 500 μM in breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) and moderately significant activity in colon cancer cells (HCT-116) cytotoxicity assays. Since, there was relatively higher cytotoxic activity in colon cancer cell lines, the cytotoxic effects of these two compounds were further evaluated under PGE2 induced conditions in two colon cancer cell lines: HCT-116 cells (IC50 values of 46 µM and 50 µM for compounds 1 and 14, respectively) and HT-29 cells (IC50 values of 37 µM and 4.5 µM for compounds 1 and 14, respectively) which signifies the possible relevance of the prostanoid inhibition pathway and its interference through the PGE2 induced oncogenic pathway.