Publication: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Authors: Ashton, Trent D. ; Dans, Madeline G.; Favuzza, Paola; Ngo, Anna; Lehane, Adele M. ; Zhang, Xinxin; Qiu, Deyun; Chandra Maity, Bikash (TCGLS Member); De, Nirupam (TCGLS Member); Schindler, Kyra A.; Yeo, Tomas; Park, Heekuk; Uhlemann, Anne-Catrin ; Churchyard, Alisje; Baum, Jake; Fidock, David A.; Jarman, Kate E.; Lowes, Kym N.; Baud, Delphine; Brand, Stephen; Jackson, Paul F.; Cowman, Alan F.; Sleebs, Brad E.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c02092
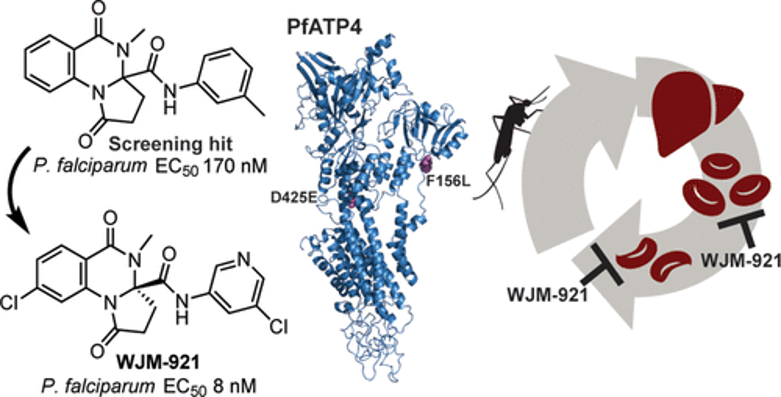
Abstract: There is an urgent need to populate the antimalarial clin. portfolio with new candidates because of resistance against frontline antimalarials. To discover new antimalarial chemotypes, we performed a high-throughput screen of the Janssen Jumpstarter library against the Plasmodium falciparum asexual blood-stage parasite and identified the 2,3-dihydroquinazolinone-3-carboxamide scaffold. We defined the SAR and found that 8-substitution on the tricyclic ring system and 3-substitution of the exocyclic arene produced analogs with potent activity against asexual parasites equivalent to clin. used antimalarials. Resistance selection and profiling against drug-resistant parasite strains revealed that this antimalarial chemotype targets PfATP4. Dihydroquinazolinone analogs were shown to disrupt parasite Na+ homeostasis and affect parasite pH, exhibited a fast-to-moderate rate of asexual kill, and blocked gametogenesis, consistent with the phenotype of clin. used PfATP4 inhibitors. Finally, we observed that optimized frontrunner analog WJM-921 demonstrates oral efficacy in a mouse model of malaria.
Graphical Abstract: