Schwertz Geoffrey; Siggel Marc; Zwyssig Adrian; Diederich Francois; Witschel Matthias C; Aponte Raphael A; Rottmann Matthias; Schafer Anja; Rottmann Matthias; Schafer Anja; Bonnert Roger; Leartsakulpanich Ubolsree; Chitnumsub Penchit; Jaruwat Aritsara; Ittarat Wanwipa; Charman Susan A; White Karen L; Kundu Abhijit (TCGLS Member); Sadhukhan Surajit (TCGLS Member); Lloyd Mel; Freiberg Gail M; Srikumaran Myron; Chaiyen Pimchai
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00008
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2017, 60(12), 4840-4860
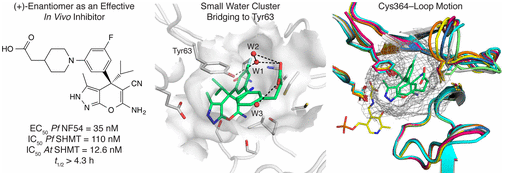
Abstract: Target-based approaches toward new antimalarial treatments are highly valuable to prevent resistance development. We report several series of pyrazolopyran-based inhibitors targeting the enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT), designed to improve microsomal metabolic stability and to identify suitable candidates for in vivo efficacy evaluation. The best ligands inhibited Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) and Arabidopsis thaliana (At) SHMT in target assays and PfNF54 strains in cell-based assays with values in the low nanomolar range (3.2-55 nM). A set of carboxylate derivatives demonstrated markedly improved in vitro metabolic stability (t1/2 > 2 h). A selected ligand showed significant in vivo efficacy with 73% of parasitemia reduction in a mouse model. Five new cocrystal structures with PvSHMT were solved at 2.3-2.6 ÅA resolution, revealing a unique water-mediated interaction with Tyr63 at the end of the para-aminobenzoate channel. They also displayed the high degree of conformational flexibility of the Cys364-loop lining this channel