Published in: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Volume 303, April 2025, 140469
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140469
Authors: Shayeri Chatterjee Ganguly, Soumya Ganguly[TCGLS Member], Beduin Mahanti, Purna Chandra Pal, Swarnajit Dutta, Subhabrota Majumdar
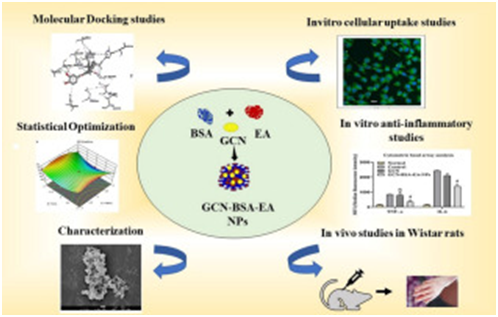
Abstract: Albumin, an excellent nanocarrier in the genre of drug delivery, endows high biocompatibility, non-immunogenicity, biodegradability, and safety. This study aims to explicate the anti-inflammatory potential of hydrophobic garcinol. Nanostructures were fabricated by an improved desolvation technique, using varied concentrations of bovine serum albumin, egg albumin, and crosslinked, for enhanced stability. Optimization through response surface methodology was carried out to obtain the best batch, considering the drug release at 8 Hrs, 16 Hrs, and encapsulation efficiency of nanoparticles as responses. Characterization was followed by drug release studies, in vitro anti-inflammatory cell line studies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, cytometric bead array analysis and in vivo investigations in carrageenan-induced paw edema. The findings revealed a size of 211 nm, a polydispersity index of 0.4, with substantial drug loading and entrapment efficiency. Drug release was controlled for 24 Hrs, without any burst effect. In silico study suggested that garcinol downregulates COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-6, which has been affirmed by the outcomes of cell line studies. In vivo investigation sketched the substantial therapeutic efficacy of the nanoparticles in ameliorating paw edema. Therefore, the efficacy of nanostructures, at the diminished dose advocated the impactful cogency of optimized garcinol-incorporated albumin-blended nanocarriers in drug delivery for combatting inflammation.



.jpg ?>)
.jpg ?>)
